IIoT, or the Industrial Internet of Things, is a revolutionary technology steadily reshaping various industrial sectors from transportation to manufacturing to energy management and beyond. Sometimes referred to as “industrial internet” or “Industry 4.0,” IIoT uses smart sensors and machines, real-time analytics, and connected actuators to improve industrial and manufacturing processes.
This guide will provide an in-depth exploration of the Industrial IoT, with a review of its benefits, limitations, and, most importantly, its potential to revolutionize industries worldwide.
What is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a subcategory of the broader Internet of Things (IoT). IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other items embedded with sensors and software that allow them to connect, interact, and exchange data over the internet.
IIoT is similar, but it focuses specifically on industrial applications. It allows manufacturing devices to be remotely monitored, controlled, and automated via connected sensors and actuators. IIoT is often used to improve:
- Quality control
- Sustainability practices
- Supply chain tracking and efficiency
- Predictive maintenance
- Energy management
- Asset tracking
How Does IIoT Work?
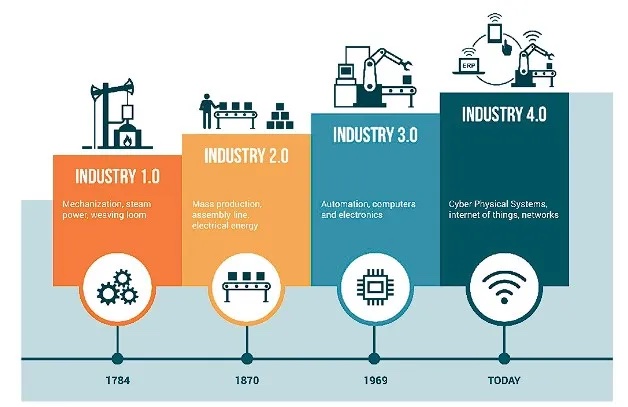
At its core, the IIoT works by connecting industrial assets to the digital world, a process often referred to as machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. Assets range from a simple sensor or manufacturing line to complex smart grids regulating energy management.
These internet-connected devices collect crucial data through embedded sensors. This data is then transmitted via cloud computing to software applications that can analyze it in real time. The end goal? To identify inefficiencies, predict issues before they happen (predictive maintenance), and devise optimal business decisions.
With artificial intelligence and advanced analytics, the collected data is processed and ‘understood’ in the context of complex industrial operations. This process facilitates immediate issue resolution and predictive strategies that drastically reduce costs and enhance customer satisfaction.
Industrial IoT Examples
While the concept of Industrial IoT might seem abstract, its applications are widespread and often closer to home than one might think. The following examples provide a glimpse into the transformative power of IIoT across industries:
- Manufacturing: IIoT is a game-changer in the manufacturing industry. With internet-connected sensors, manufacturers can monitor equipment health, track inventory, and streamline production workflows. For example, an IoT-enabled assembly line could automatically alert managers when a part is due for replacement.
- Automotive: IIoT is reshaping the automotive landscape, from smart automotive factories implementing predictive maintenance to connected vehicles providing real-time diagnostics. IIoT aids in enhancing safety features by tracking vehicle performance and alerting drivers about potential issues.
- Energy Management: IIoT plays a crucial role in modern energy infrastructure. It enables utilities to monitor energy usage, predict demand, and efficiently manage energy distribution. For example, smart grids use IIoT to monitor and control real-time electricity generation and distribution.
- Agriculture: Smart farming techniques involve internet-connected devices monitoring crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. Using IIoT, farmers can make informed decisions about watering schedules, fertilizer application, and harvest timing based on real-time data.
- Healthcare: IIoT is used in healthcare for remote patient monitoring, equipment tracking, and predictive maintenance of medical devices. By gathering and analyzing patient data in real-time, healthcare providers can offer more personalized treatment plans and predict potential health issues before they escalate.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: IIoT aids in tracking goods in real time, monitoring the condition of cargo, and optimizing delivery routes. This level of visibility reduces costs, improves customer satisfaction, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
These examples barely scratch the surface of IIoT’s potential. As technology advances and more industries recognize the value of digital transformation, IIoT is bound to find more applications.
Benefits of IIoT
By harnessing the power of internet-connected devices and artificial intelligence, IIoT brings a wealth of advantages beyond mere operational efficiency.
1. Regulatory Compliance
Navigating regulatory compliance can be daunting for organizations. IIoT can simplify compliance management by enabling continuous monitoring of key parameters, such as emission levels and waste disposal in manufacturing that help ensure environmental and safety standards.
In healthcare, IIoT helps certify HIPAA compliance through secure, encrypted transmission of patient data. Automated, real-time data collection can minimize human error, allow for proactive issue identification and resolution, conserve resources, and shield businesses from fines and reputational damage.
2. Digital Workforce Efficiency
Connecting employees with a digital infrastructure fosters improved productivity and collaboration through seamless inter-departmental communication and access to real-time data, enabling quick decision-making.
The manufacturing and automotive industries can leverage IIoT-powered virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for precision training to help minimize errors. Predictive maintenance features of IIoT devices also prevent unexpected equipment failures, reducing work delays.
3. Product Quality
IIoT offers manufacturers a significant opportunity to enhance quality control and assurance. Real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes using IIoT sensors can track variables like temperature and pressure to enable quick corrective action for any quality deviations.
Predictive analytics offered by IIoT helps businesses foresee potential quality issues, optimize processes, reduce defects, and increase customer satisfaction while minimizing costs. Especially in sectors like automotive IoT, real-time quality control can critically influence product success and impact a company’s reputation and financial performance.
4. Remote Condition Monitoring
IIoT facilitates remote condition monitoring, allowing businesses to track equipment performance in real time. Any changes or abnormalities, such as deviations in vibration or temperature, can be promptly identified and addressed.
This application is transformative in industries like transportation and logistics, where shipping companies can monitor and adjust cargo conditions to prevent spoilage. Similarly, in energy management, smart grids use IIoT to monitor components, reducing equipment failure risks and service interruptions while extending equipment lifespan and cost savings.
5. Real-time Data Collection & Processing
Industrial IoT boosts data-driven decision-making by collecting and analyzing real-time data from industrial operations, providing detailed insights into machine functioning, process efficiency, and product behavior. This data is processed and analyzed using artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify patterns, predict trends, and generate actionable insights.
Real-time data collection and processing can enhance operational efficiency, facilitate a deeper understanding of business processes, and enable continuous improvement, leading to long-term business success.
6. Worker Safety
IIoT significantly enhances worker safety in hazardous industries like manufacturing, mining, or construction. Wearable IIoT devices monitor workers’ vital signs and exposure to harmful conditions, giving real-time alerts for prevention. Thermal imaging can detect overheating equipment or electrical faults for timely maintenance and accident prevention.
IIoT also increases safety for remote workers through real-time tracking and communication, enabling rapid emergency response. Thus, IIoT not only ensures worker safety but also minimizes operational disruptions to boost overall business efficiency and productivity.
7. Predictive Quality & Maintenance
Utilizing advanced analytics and AI, IIoT can predict failures, schedule maintenance, and collect real-time data to monitor product parameters, identifying potential quality issues like changes in temperature or humidity.
Predictive maintenance revolves around anticipating equipment wear and tear and scheduling maintenance during non-peak times to reduce costs and downtime. The predictive capabilities of IIoT are shifting industries from a reactive to a proactive approach, optimizing operations, reducing costs, and enhancing product and process standards.
Industrial Internet of Things Limitations
While the benefits of IIoT are immense, it’s essential to understand that it isn’t without its challenges. As businesses venture further into the realm of IIoT, they encounter a set of limitations that can impact the effective implementation of this technology.
Let’s take a closer look at these challenges:
- Security and Privacy Concerns: The rise in connected devices introduces more potential entry points for cyberattacks and data protection challenges. Businesses must invest in robust security measures such as data encryption, secure user authentication, and regular system updates. For example, ZeroTier addresses these concerns by using advanced encryption and secure protocols, ensuring a safe network for IIoT devices.
- High Initial Costs: The cost of implementing IIoT technology can be substantial. It includes the price of sensors and devices, data storage and processing capabilities, and possibly new personnel or training for current staff.
- **Need for Skilled Workforce: **Managing and interpreting the vast amounts of data produced by IIoT requires a skilled workforce. There’s a growing need for professionals with expertise in data analysis, machine learning, and other related fields.
- Integration Challenges: Many businesses struggle with integrating IIoT technology with existing systems and processes. This can result in a disjointed and less efficient operation. However, software that connects IIoT devices, like ZeroTier, can provide platforms compatible with various devices, facilitating seamless integration.
- Infrastructure Limitations: In some regions, limited internet connectivity and inadequate infrastructure can hinder the successful implementation of IIoT solutions.
- Regulatory Challenges: Depending on the industry and region, businesses may face regulatory challenges related to data privacy, security, and usage.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of IIoT for businesses and society at large far outweigh the limitations. With a strategic approach and the right tools, businesses can navigate these challenges successfully and harness the full power of IIoT.
How to Connect Your IIoT Devices
Integrating IIoT devices into your industrial operations is a strategic process that requires careful planning and the right software. The goal is to establish a secure, reliable, and efficient system that seamlessly collects and analyzes data, offering valuable insights to drive your business forward.
ZeroTier is a leading platform designed to create secure networks for your IoT devices. It simplifies the task of connecting your devices by creating a global, private network over the internet. Whether your devices are across different locations or on the move, ZeroTier ensures they are connected securely and consistently.
The implementation process is straightforward:
- **Installation: **Install the ZeroTier software on your devices.
- Join Network: Each device is assigned a unique address and can be added to your private ZeroTier network.
- Manage Devices: Through the ZeroTier central interface, you can manage your devices, check their status, and even configure network rules.
With ZeroTier, you don’t have to worry about the complex task of creating VPNs or configuring firewalls. It makes connecting your IIoT devices simple, secure, and cost-effective, enabling you to leverage the full potential of the industrial internet and drive your business’s digital transformation.
FAQ on IIoT


Here we address some common questions about the Industrial Internet of Things, providing a clearer understanding of what it entails and its implications.
What is the Difference Between IoT and IIoT?
IoT generally refers to consumer-level devices, like smart home appliances and wearables. IIoT, on the other hand, is focused on industrial applications.
What is Industrial IoT Architecture?
Industrial IoT architecture is the structure that outlines how various IIoT components, including sensors, devices, networks, and applications, interact. A typical IIoT architecture comprises four layers:
- Edge layer: This is where the physical devices, sensors, and actuators are. They collect data and perform actions.
- **Communication layer: **This layer handles the transmission of data from the edge layer to the processing layer.
- **Data Processing and Analytics layer: **Here, the collected data is processed, analyzed, and stored. This layer often involves cloud computing and can leverage artificial intelligence for advanced analytics.
- Application layer: This is the user-facing layer where actionable insights are provided. It can include dashboards, alerts, or automation controls.
The architecture can vary based on specific requirements, but the goal is always to facilitate secure and efficient data flow from the physical world to the digital, and vice versa.
Is IIoT Secure?
Like any other digital technology, IIoT faces security challenges. The interconnected nature of IIoT creates potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. However, with robust security measures in place, such as data encryption, secure user authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular system updates, IIoT can be made secure.
Moreover, choosing a reliable and secure connectivity platform, such as ZeroTier, adds an extra layer of security, ensuring your IIoT network and the valuable data it generates remain protected.
Securely Connect All Your IIoT Devices
The Industrial Internet of Things is reshaping the landscape of various industries by enabling smarter, more efficient, and more secure operations. Despite the challenges associated with implementing IIoT, the benefits it offers in terms of operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, product quality, and worker safety make it a compelling investment for any forward-thinking enterprise.
As you navigate the implementation of IIoT, choosing the right platform for secure and reliable connectivity is crucial.
ZeroTier offers a robust solution that simplifies the process of connecting your IIoT devices, irrespective of their location. With its user-friendly interface and high-security protocols, you can focus less on the complexities of network configuration and more on leveraging the benefits of IIoT for your business.

